
The effective management of information is not only essential but also pivotal for the success of any organization. It plays a crucial role in enhancing the customer experience, improving employee morale and efficiency, and maintaining competitiveness in the market. This article provides an insightful overview of knowledge management (KM) and aims to assist in selecting the most suitable knowledge management tool for consistently maintaining a competitive edge.
Understanding Knowledge Management

Knowledge Management (KM) is truly fascinating as it involves the effective acquisition, generation, distribution, and utilization of knowledge. It focuses on leveraging institutional knowledge to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and facilitate informed decision-making. KM applies to both organizations and individuals, underpinning various aspects such as internal processes, customer engagement, and marketing content creation.
Types of Knowledge
In the business realm, understanding the different types of knowledge is crucial for fostering innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. Here’s how they play out:
- Tacit Knowledge: Found within the minds of employees, tacit knowledge encompasses the skills, experiences, and insights that are difficult to capture and articulate. It’s the know-how that workers gain over time, which can be a goldmine for businesses when leveraged through mentorship programs and collaborative work environments.
- Implicit Knowledge: This is the unspoken understanding that employees develop through their roles. It includes the routines, practices, and norms that are known within a team but not formally recorded. Businesses can tap into this knowledge by encouraging a culture of sharing and creating avenues for employees to communicate their insights and work habits.
- Explicit Knowledge: The most transferable form of knowledge, explicit knowledge includes all the documented information that a business relies on, such as SOPs, manuals, databases, and reports. It’s the foundation for training, compliance, and scalability. Companies should invest in knowledge management systems to capture, store, and disseminate this valuable resource effectively.
By recognizing and nurturing each type of knowledge, businesses can create a robust knowledge management strategy that supports growth and adaptation in a dynamic marketplace.
Exploring the Multifaceted Nature of Knowledge Management
Knowledge Management (KM) is a complex domain that intertwines various aspects of how organizations handle information, expertise, and wisdom. The implementation of the right KM software offers a myriad of advantages, including increased knowledge retention, quicker decision-making, enhanced productivity, continuous business growth, better team alignment, and maximized security. These incredible benefits contribute to a superior customer experience, as employees are well-informed and prepared to address challenges, leading to a positive impact on the organization’s success. So, what are the best KM practices and tools?
Document Management Tools
Document management is a fundamental aspect of business operations, with platforms like Microsoft SharePoint at the forefront. SharePoint is a powerful tool for document storage, retrieval, and collaboration, ensuring that the right documents are always accessible, up-to-date, and managed with robust version control and permissions, which is crucial for maintaining efficiency and promoting seamless workflows.
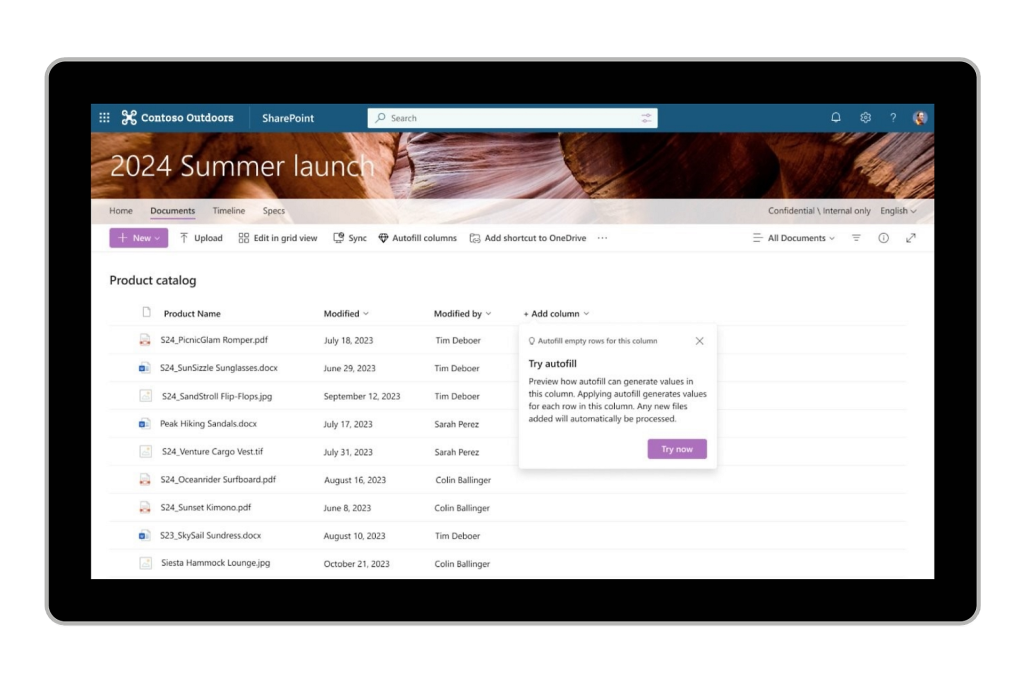
Collaboration Tools
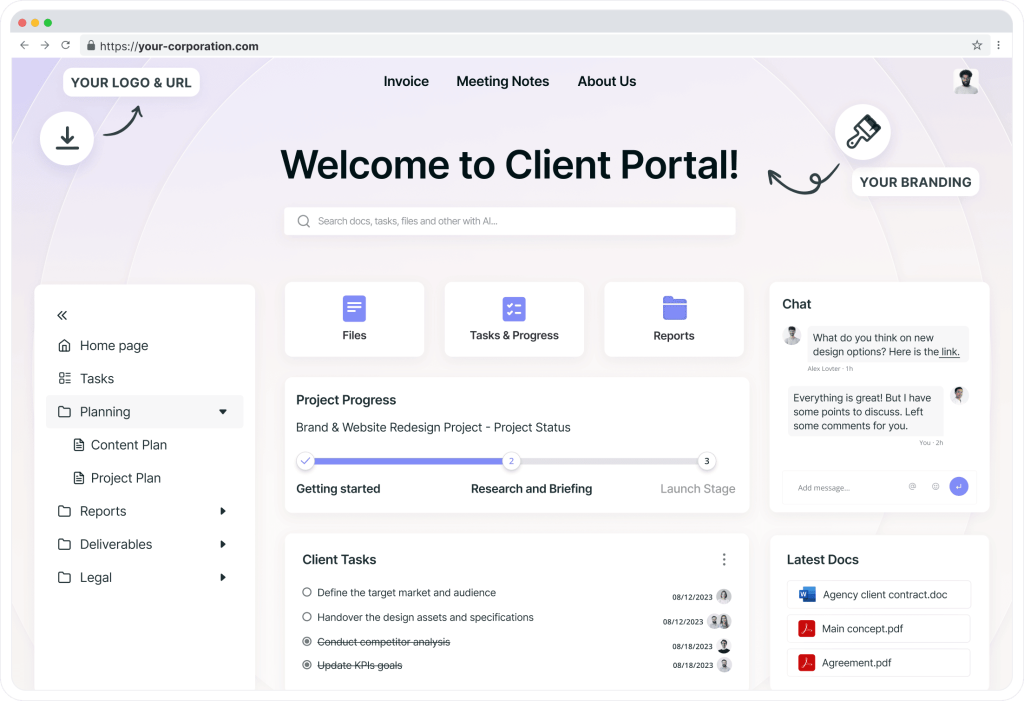
Collaboration tools play a crucial role in the effective sharing and utilization of knowledge, which in turn enhances organizational performance and decision-making. FuseBase is one such tool that enhances team collaboration by integrating knowledge management directly into the workflow, fostering a connected and informed work environment.
Internal Knowledge Base
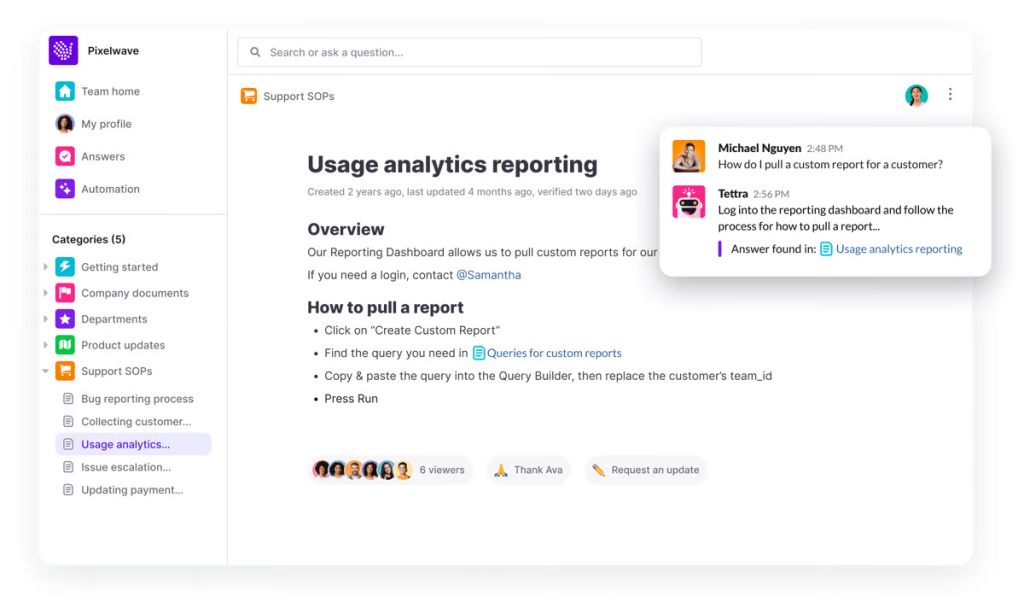
An internal knowledge base, or “wiki,” is a central repository for internal articles, procedures, processes, and training materials. Tettra stands out in this category as a knowledge management system that is especially designed for Slack users, providing a centralized place for internal documentation and SOPs, and fostering a culture of shared expertise within organizations.
Content Management Tools
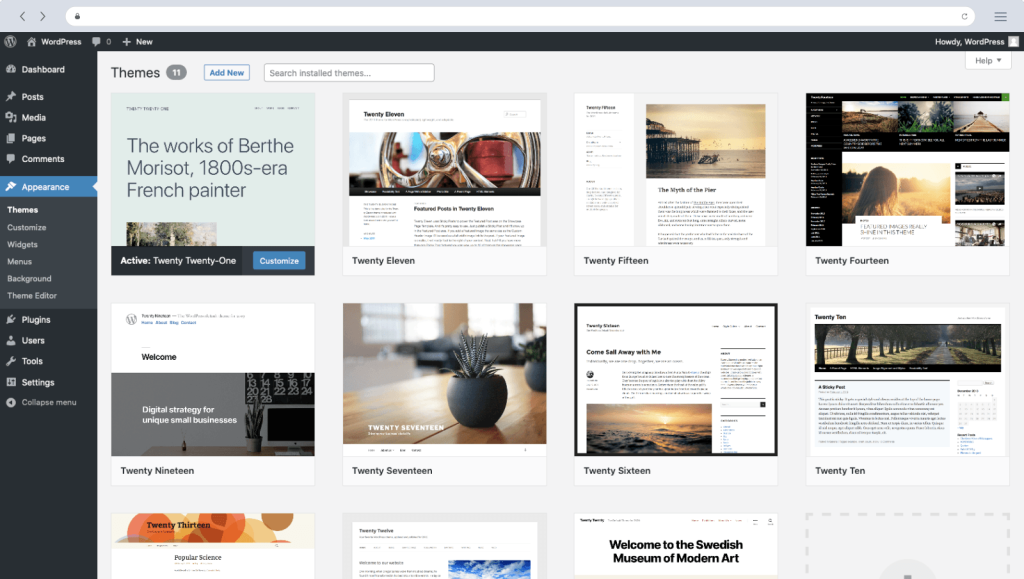
Content management is a vital part of knowledge management, involving the creation, formatting, storage, and publishing of content. WordPress is a popular and highly customizable content management system that excels in creating and managing websites and blogs, facilitating effective communication and knowledge sharing.
Automation Tools
The integration of automation and AI-powered tools into knowledge management is transforming organizational processes. Zapier exemplifies this transformation by connecting various apps and automating workflows, allowing for the streamlining of repetitive tasks without the need for complex coding, thereby heralding a new era of productivity.
Inventory Management Tools
Inventory management is key to managing operational costs and ensuring customer satisfaction. NetSuite provides a comprehensive business management suite that includes features for inventory, warehouse management, and financials, which are essential for understanding inventory levels and procurement schedules, and for paving the way for streamlined operations.
Project Management Tools
Effective project management is critical for the success of internal initiatives and for delivering value to customers and stakeholders. Asana is a project management tool that aids teams in organizing, tracking, and managing work with tasks, projects, and deadlines, ensuring that every stage of the project lifecycle is supported and successful.
Summary
The choice of knowledge Management tool depends on the current needs of the business. Each tool can solve several needs simultaneously, but these are not universal solutions. So choose several tools that will help effectively manage the business.

